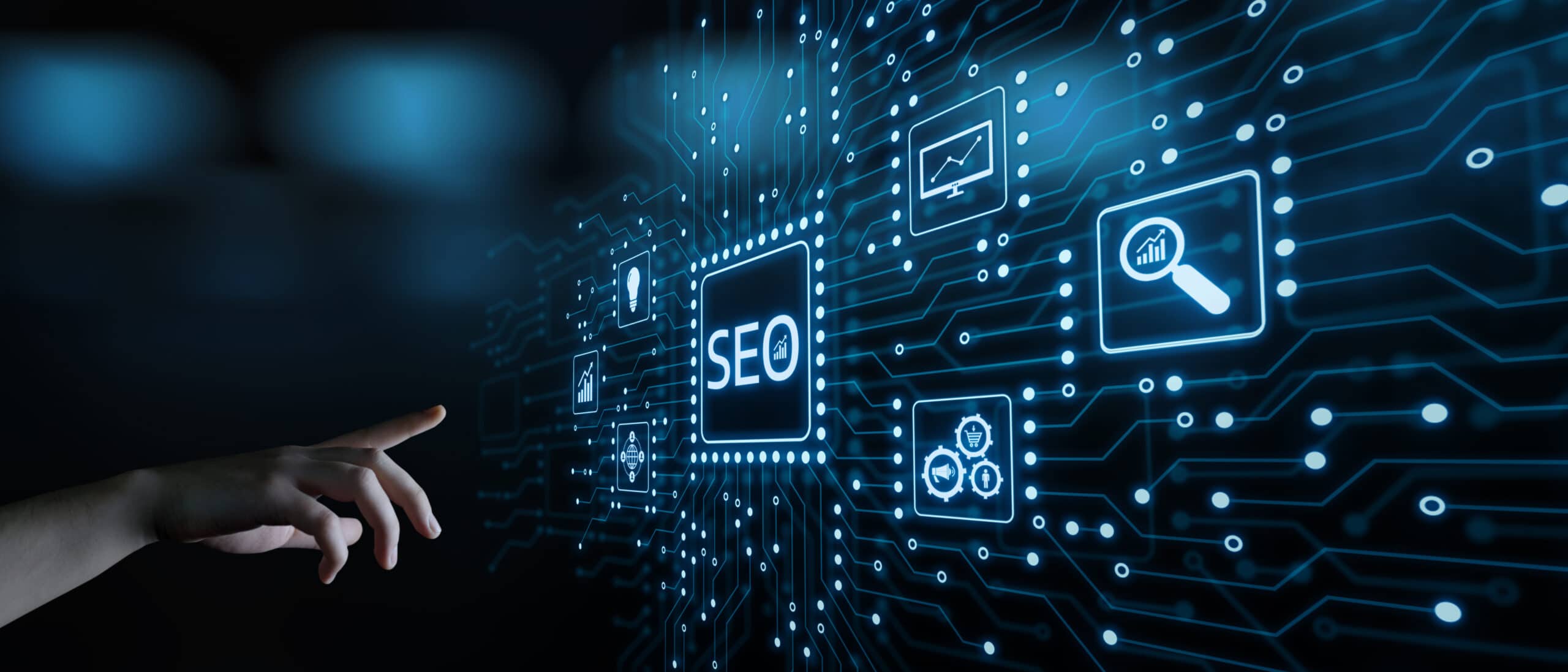
Reverse SEO is one of the many methods of managing online reputation, but with a twist. Instead of going at the negative comments and content about your business, you drown it out with positive comments. Think of it this way, for every negative piece of content about your business on the internet, you create ten positive contents and promote them. This way, when people search about your website, they only see positive content.
Understanding the basics of reverse SEO:
Reverse SEO is a technique for managing your online reputation by improving other websites or pages for the same target keyword to push down the negative reviews. It’s used by reputation management firms and online public relations specialists to manage how people perceive a person or brand. With Reverse SEO, negative reviews and press releases are buried deep into the listings so that fewer people see them. As the newly improved web pages rank higher in Google, the bad review or press release will begin ranking lower.
You usually can’t remove a negative review or press release from Google or Bing search results unless it violates their rules. Contacting the author and resolving the issue that prompted their bad opinion about your company is a typical reputation management best practice. However, neither Google nor Bing will remove it from their search results, assuming the author complied with Google and Bing’s guidelines. The good news is that you can avoid having your company’s reputation damaged by negative reviews and press releases by utilizing reverse SEO online.
Understanding the difference between Reverse and Negative SEO
Reverse SEO is sometimes mistaken with negative SEO, although they have distinct objectives and require different strategies. For Reverse SEO, you build and optimize positive web pages to bury bad reviews and news about your company. On the other hand, Negative SEO is a blackhat practice where you attempt to decrease a competitor’s search rankings by producing a lot of low-quality backlinks.
Negative SEO is also against search engine regulations. You can’t create bad backlinks to a competitor’s website with an intention to damage their search rankings. If your firm is discovered engaging in negative SEO, search engines may punish your site’s position in the search results while removing the impact of any negative backlinks you established to your competition’s site.
How to Perform Reverse SEO
Once you’ve discovered a negative review, press release, or another website that is damaging to your company’s reputation, start a reverse SEO campaign. Begin by determining the specific keywords that drive search rankings for the negative web page. If you have access to Moz or SEMrush, you can utilize one of their rank-tracking tools. Regardless, make a list of all the keywords for which the negative web page ranks highly in Google searches.
Consider optimizing your company’s website to rank highly for your company’s name if a negative review appears on Google’s first page. If there is no website for your company, create one using its precise spelling as the domain. Create and optimize subpages for long-tail keywords on your business’s website, whether with or without the name. If a bad web page ranks highly for the brand name of an exclusive product or service offered by your firm, you may build a new page on your site and optimize it for the brand name.
You can also use SEO to improve your company’s website, as well as other online properties. Reverse SEO is considerably more straightforward when you have a solid social media presence. You may frequently get your business’s Facebook and Twitter accounts to appear at the top of search results with little effort.
The longer you wait, the worse it gets
The greater the delay in starting a reverse SEO campaign, the longer a negative media release sits unchallenged at the top of search results. It will be easy to lower their search ranks if you target harmful websites as soon as they’re indexed.
But how can you tell when new negative reviews or press releases about your business are published?
You may always manually search for your company’s name and look for the top-rated results. Alternatively, you may set up Google Alerts for any mentions of your company’s name to receive a notification. If Google discovers new content mentioning your firm’s name, it will send you an email with a link to that page, which you can then use reverse SEO on.
To set up a Google Alerts, go to google.com/alerts and log in to your Google account. Enter your company’s name in the “Alerts” box. To narrow down irrelevant alerts, put them in quotation marks. You may also want to create Google Alerts for the names of your company’s goods and services if you don’t already have them set up.
According to Google, the first page of search results accounts for over nine out of ten organic clicks. If a bad web page about your company ranks on Google’s or Bing’s top page, it will most certainly cost you money. And if you don’t want to, you should use reverse SEO to lower the rankings of negative web pages and protect your business from losing revenue. Even if a bad review or press release is only listed on the second page of search results, it will receive far fewer views than if it were on the first page.